Benefits of barcode inventory system
Why have businesses been slow to adopt barcode inventory systems? Read on to find out some of the benefits that barcode inventory software provides.


Discover the benefits of AccelGrid

Convert more leads into revenue

Manage orders at scale

Streamline billing and get paid on time
Rock-solid inventory control

Optimize your supply chain
Switch to lean manufacturing

Sell anywhere, anytime with mobile POS

Simplify accounting and grow your business

Sell more with integrated eCommerce

AI-powered demand forecasting
Convert more leads into revenue
Manage orders at scale
Rock-solid inventory control
Streamline billing and get paid on time
Optimize your supply chain
Achieve lean manufacturing
Sell more with integrated eCommerce
Sell anywhere, anytime with mobile POS
AI-powered demand forecasting
Simplify accounting and grow your business
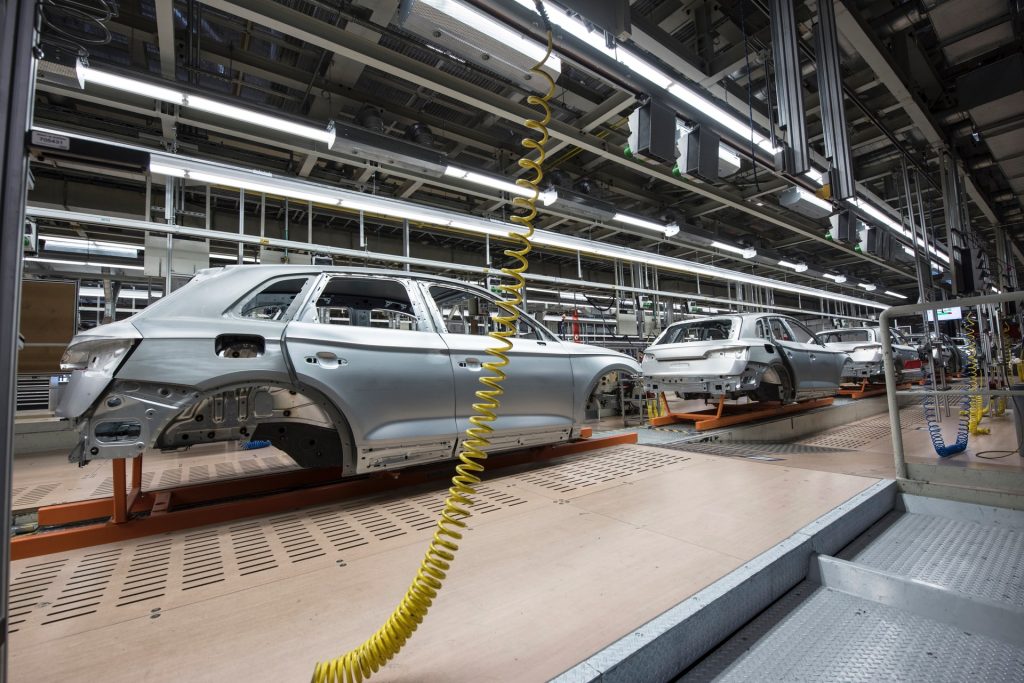

Lean manufacturing is a production process centered around maximizing productivity and minimizing waste. Many manufacturers have adopted the principles behind lean manufacturing across the globe to achieve manufacturing excellence. Automobile manufacturer Toyota pioneered lean manufacturing concepts and systems back in the 1940s. Owing to the benefits that lean manufacturing offers, many other industries have followed Toyota’s footsteps to adopt it subsequently.
But is implementing a lean manufacturing process right for your business? This article will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of lean manufacturing to help you decide whether it is suitable for your business.
Lean principles aim to minimize all forms of waste. Waste can include everything from overstocking to material defects to worker ergonomics. While many sources of waste are easy to identify and correct, it takes a lot of attention to detail to discover some subtle sources of waste. Companies typically sit on large amounts of inventory and waste. Lean manufacturing eliminates aged inventory and significantly reduces operating costs. A lean infrastructure also means using the right number of components such as building, tools, supplies, equipment, and labor to fulfill near-term demand. More productivity with less waste eventually translates into a more profitable company.
The lean manufacturing process requires ‘buy-in’ and participation from your production team. Involving your workers in the improvement process is a great way to promote a sense of responsibility and ownership. Process ownership leads to increased work satisfaction and improves productivity.
By streamlining manufacturing processes, businesses can better respond to fluctuations in demand and other variables. An essential pillar of the lean approach to manufacturing is JIT (Just in Time) inventory to minimize waste. JIT means that raw materials are purchased and made available only when production needs them. Adopting lean manufacturing helps you build a transparent supply chain that focuses on building solid relationships with suppliers who can support your Just In Time inventory demands.
The benefits of lean manufacturing go beyond reducing costs and improving efficiency. Lean manufacturing can help you gain a competitive edge over your competition by enabling you to produce and deliver high-quality products with minimum waste and shorter iterations.
A classic example of ‘the solution becoming the problem’ is when tracking productivity and waste starts to impact the time used for production. Companies typically experience significant returns when lean principles are first applied. To increase efficiency and profitability, some companies often push the expectations to unrealistic limits that do more harm than good.
JIT principles work best when you have a transparent supply chain. When the lead times for raw materials and finished goods are predictable, it is easier to schedule production and commit accurate lead times to your customers. However, an overly optimistic JIT scheduling can result in bottlenecks and production stoppages. Systemic delays such as supplier delivery issues and maintenance emergencies can reduce your production throughput. Accounting for such constraints in your JIT planning is critical to avoid production delays.
Implementing lean manufacturing often means dismantling existing processes, shopfloor setups, equipment, and systems. Acquiring and training employees and managers is often a long-winded process that can add to your companies’ payroll expenses. Similarly, the purchase of more efficient machines can add to long-term debt. Small and medium-sized businesses, in particular, may find these additional costs prohibitive to switch over to lean production.
All businesses are unique in terms of the challenges they face. Therefore, the benefits and downsides of lean manufacturing will vary for each organization. When implemented correctly, lean manufacturing can bring significant improvements to efficiency and profitability. A commitment to achieving manufacturing excellence, coupled with proper training and suitable ERP software, is critical to lean manufacturing implementation. Having the right processes and systems to monitor and track key manufacturing KPIs can go a long way in helping you identify bottlenecks and make continuous improvements.
A well-implemented lean production process can enable you to produce high-quality products on time, every time. It is also essential to carefully identify and examine the risks of lean production so that you can factor them into your production schedule.
Why have businesses been slow to adopt barcode inventory systems? Read on to find out some of the benefits that barcode inventory software provides.
Businesses must maintain the right amount of inventory to keep their customers happy and grow efficiently. How do you know what amount of stock is right?
Investing in inventory software with the right automation tools can help you achieve operational efficiency and eventually increase your bottom line.